User Guide
UniCa$h is a desktop application used for university students who want to be more financially conscious, optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, UniCa$h can get your finance management tasks done faster than traditional GUI apps.
Quick Start
Installation
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
unicash.jarfrom GitHub. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your UniCa$h.
-
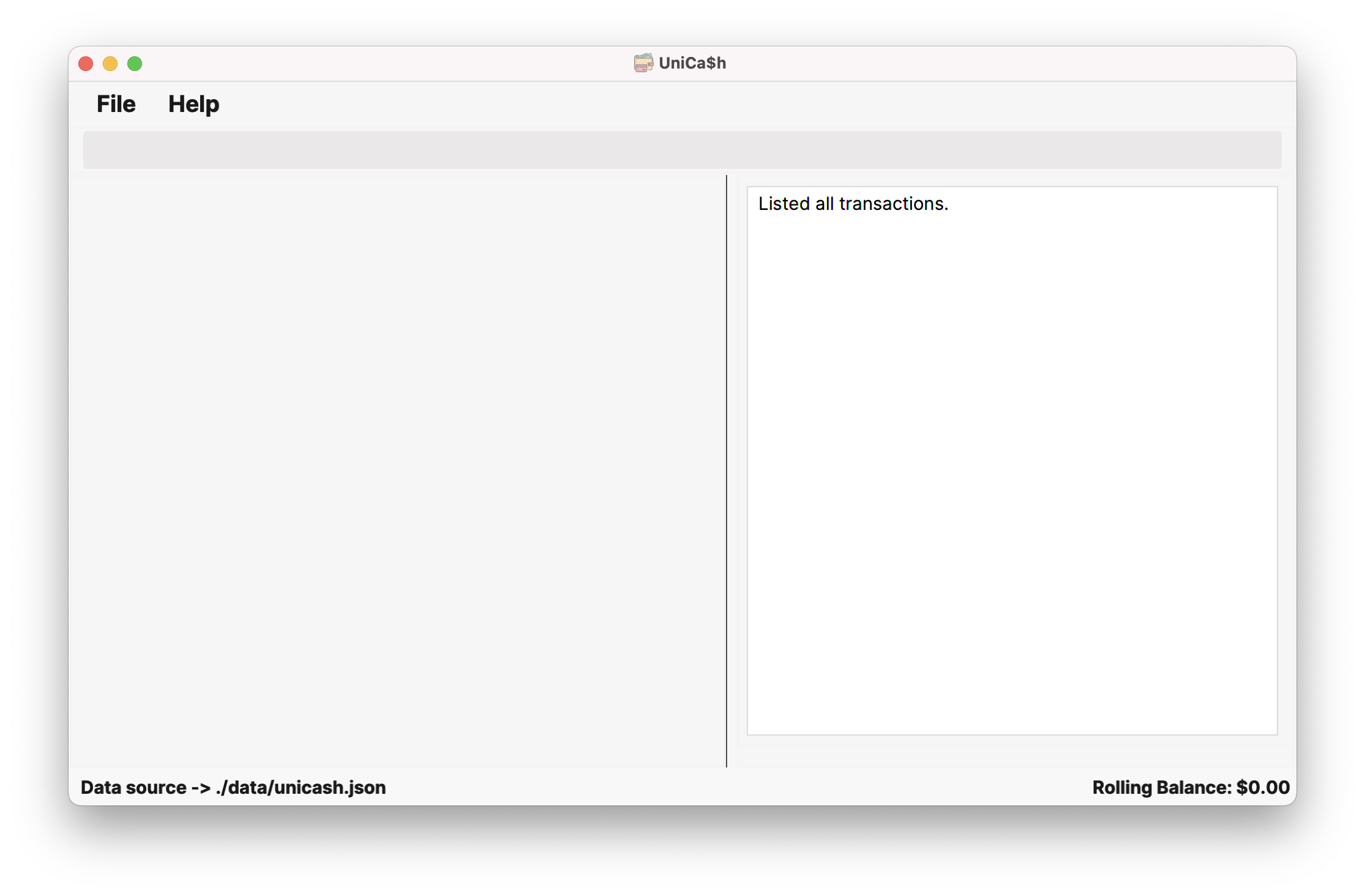
Open a command terminal,
cdinto the folder you put the jar file in, and use thejava -jar unicash.jarcommand to run the application.A GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
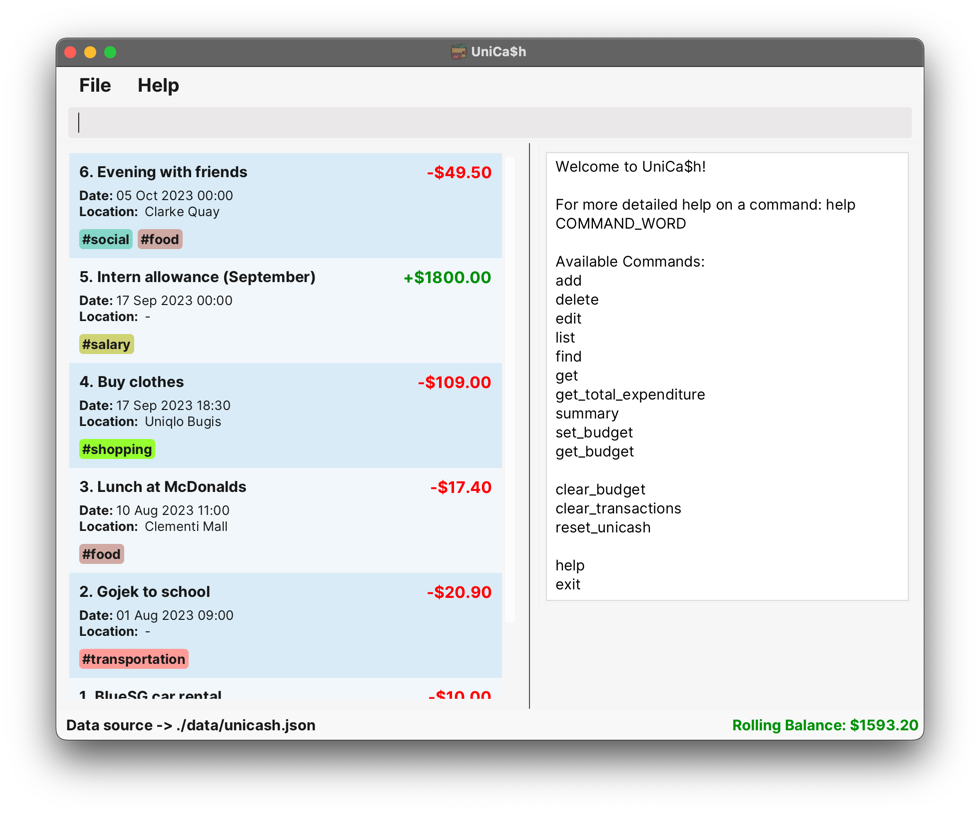
-
Type a command in the command box and press
Enterto execute it. e.g. typinghelpand pressingEnterwill execute thehelpcommand and open the help window.To get started with UniCa$h, you can run the
add_transactioncommand! -
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Command Breakdown
Commands in UniCa$h have the following structure:
command_word (ARGUMENT) (PREFIXES)
| command_word | ARGUMENT | PREFIXES |
|---|---|---|
| Represents the command to run. May be referenced by alternative shorthands as described in each command section. All commands and their alternatives are always case-insensitive. | Comes before all prefixes and often used to reference an index within the transactions list Often optional |
Often referred to as “Parameters” Commonly used to specify various attributes/properties for a given command_word |
Argument Types
| Argument | Meaning | Constraints | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
INDEX1,2 |
Index of transaction in transaction list | Integer indices that must be >= 1 (positive integer) and are one-indexed, i.e. start with 1, not 0. |
Commonly used in edit and delete to reference transactions in a transaction list |
Notes:
INDEXuses positive integers which we define as integers that are strictly greater than0.- UniCa$h divides the error handling for
INDEXinto two cases, invalid numbers (non-positive integers, i.e.<= 0values, values larger thanInteger.MAX_VALUEor non-integer values e.g.10.2) are treated as invalid command formats while values that exceed the transaction list will be treated as being an invalid index as the supported values are[1, transaction list size].
INDEX is parsed this way, please refer to our developer guide on how some commands like delete_transaction handles INDEX.
Prefixes
Prefixes are in the format:
prefix/Value
Prefixes have several variations with different notations:
| Mandatory | Optional1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Not variadic | prefix/Value |
[prefix/Value] |
| Variadic | prefix/Value... |
[prefix/Value]... |
Notes:
- Optional fields imply that the omission of the field, not the absence of value when used, is supported. This means that
l/is NOT an optional parameter, but rather a blank one.
Prefix Types
Note that each command might use the prefixes slightly differently so refer to each command’s details for more information.
| Prefix | Constraints | Remarks | Valid | Invalid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
n/(Transaction name) |
At least 1 character but no more than 500 characters. Only supports alphanumeric characters, spaces, (, ), _, @, -, #, &, ., and , characters. |
Blank names are not allowed. | n/Hi (John) |
n/n/Two ^ |
type/(Type of transaction) |
Only supported values are expense and income. |
Case-sensitive, any other values, including blank values (i.e. type/), will be rejected. |
type/expensetype/income |
type/type/EXPENSEtype/hi |
amt/1(Monetary amount of budget and transactions) |
Values must be >= 0.00 and <= 2,147,483,647. |
Supported inputs allow an optional leading $ character and all amount values are rounded to the nearest 2 decimal places so $0.001 will be treated as $0.00. |
amt/0amt/$10.09amt/$0.00 |
amt/amt/-100amt/hiamt/%0.00 |
dt/(Date & time of transaction) |
Only supported formats are: dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm, yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm, and dd MMM yyyy HH:mm |
If no value is provided, i.e. dt/, then it defaults to the current date time when the command is run, using the same date time as the user’s system clock. |
dt/dt/15-02-2023 14:30dt/2023-02-15 14:30dt/15 Feb 2023 14:30 |
dt/15 August 2023dt/ 14:30dt/15-11-2023 |
l/(Location of transaction) |
At least 1 character but no more than 500 characters. Only supports alphanumeric characters, spaces, (, ), _, @, -, #, &, ., and , characters. |
Blank locations are not allowed. Omit this prefix entirely to indicate that there is no location, l/ alone is not permitted (blank location). |
l/NTUC @ UTown |
l/l/Two ^ |
c/(Category of transaction) |
At least 1 character but no more than 15 characters. Only supports alphanumeric characters. |
Blank categories are not allowed. Omit this prefix entirely to indicate that there is no category, c/ alone is not permitted (blank category).Categories are always saved in lowercase. |
c/Hic/JustExactly15Ch |
c/c/Over15Charactersc/#books |
month/(Month that transaction was performed) |
Values must be >= 1 and <= 12 |
Assumes January corresponds to 1, February to 2 and so on. |
month/1month/10month/12 |
month/month/0month/-10month/15 |
year/(Year that transaction was performed) |
Values must be >= 1920 and <= 2,157,483,647 |
Intentional restriction to have years be >= 1920. |
year/1920year/2023 |
year/year/1919 |
interval/2(Budget interval) |
Only supported values are day, week, and month. |
Case-sensitive, any other values, including blank values (i.e. interval/), will be rejected. |
interval/dayinterval/weekinterval/month |
interval/interval/DAYinterval/hi |
Notes:
- Amounts can be exactly
$0.00as users may want to simply track that a transaction is present but not specify the amount. User might also want to track financial events not involving currency exchange, such as barter trading, free gifts, etc. - Intervals work by filtering by the specified time period.
- For
dayintervals, only transactions of the same day are found. - For
weekintervals, only transactions of the same week of year are found. - For
monthintervals, only transactions of the same month are found.
- For
User Interface (UI) Overview
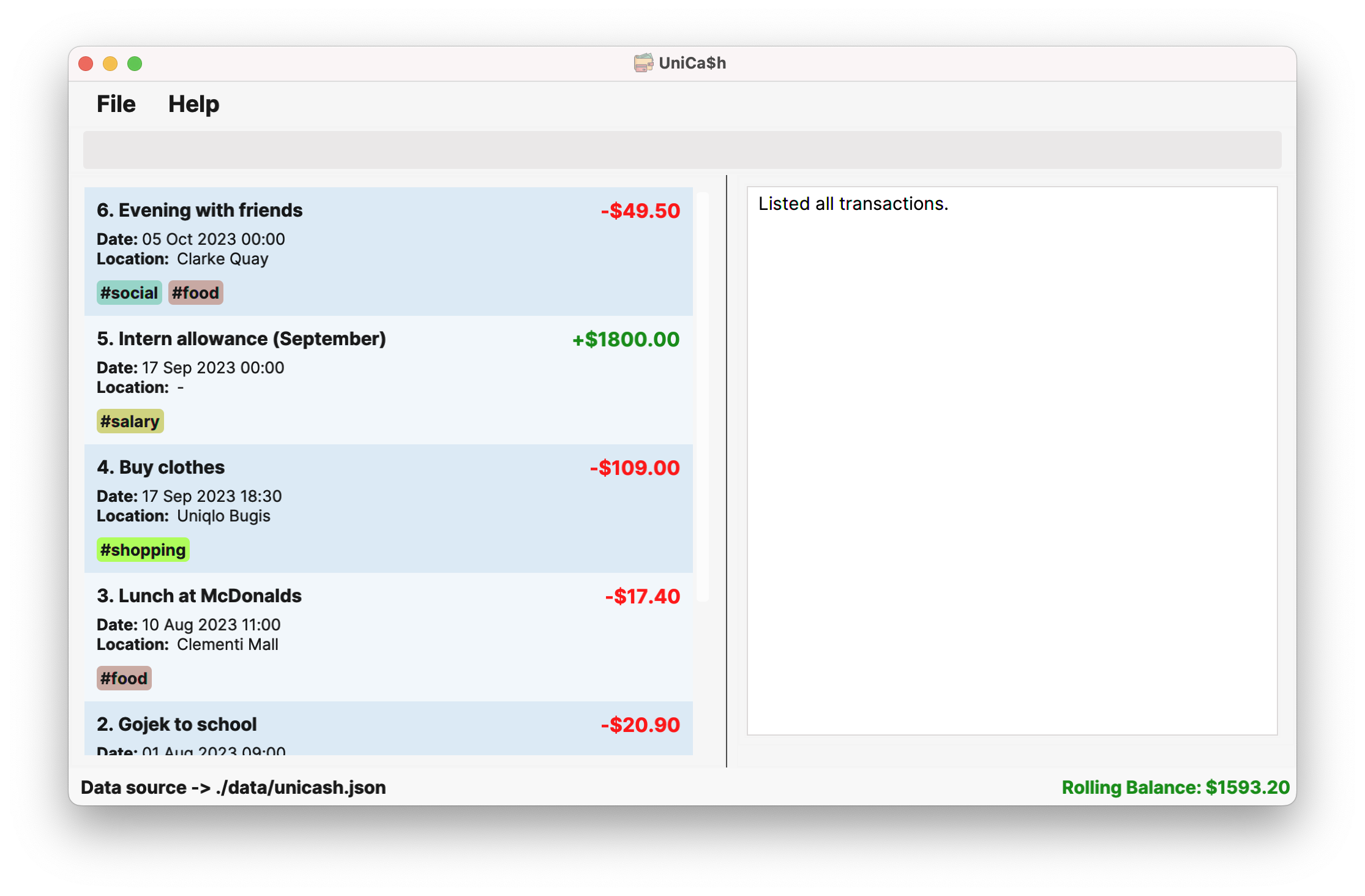
When UniCa$h is first opened, it would look something like the image shown earlier near the top of the user guide.
The UI components and features are elaborated explicitly in our Developer Guide which can be found here. However, for ease of reference of some key UI terms used in this User Guide, the annotated image of the UniCa$h window is duplicated below.
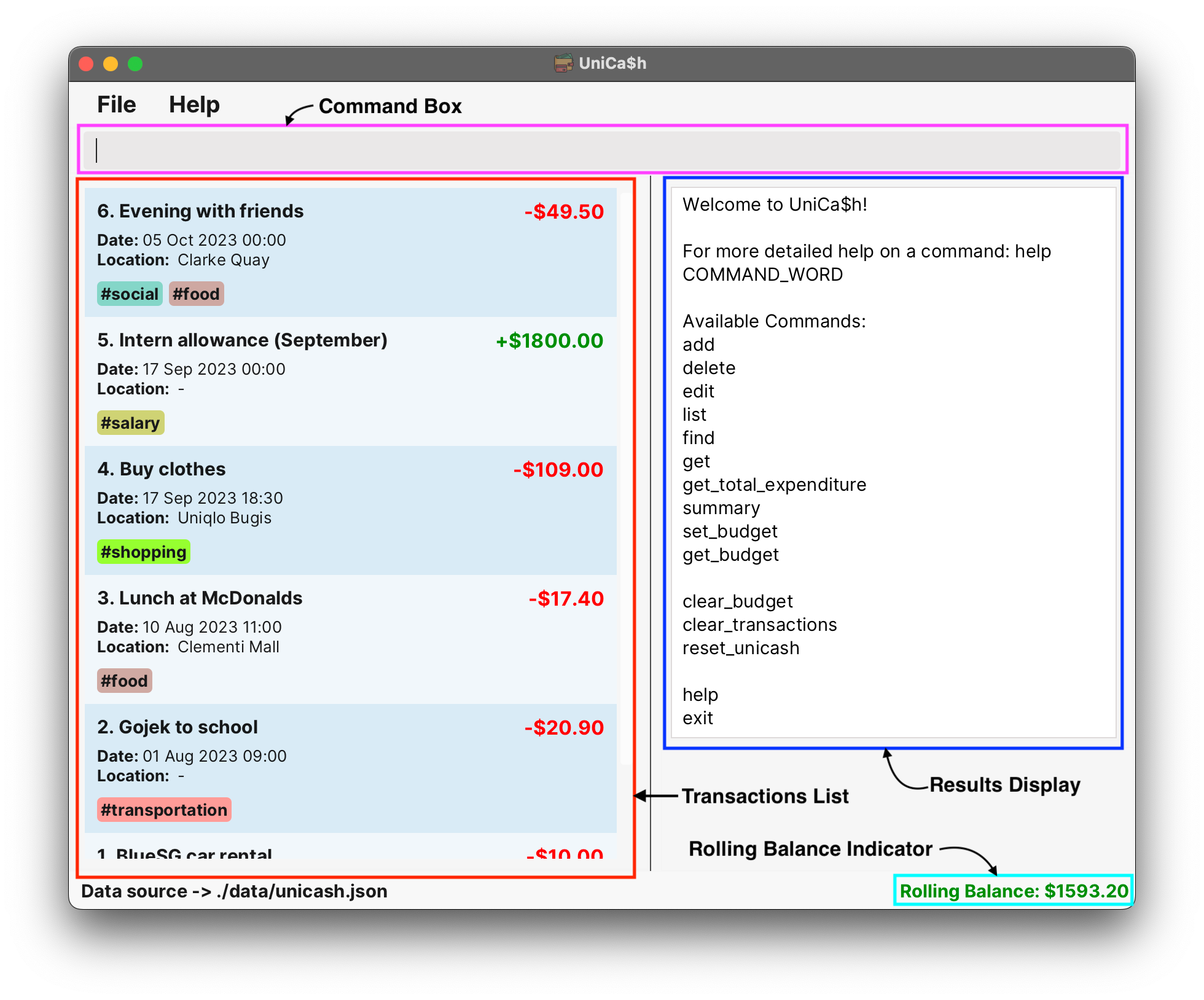
Features
Features Overview
UniCa$h comprises four primary feature groups:
- Transaction Management
- Add Transaction (
add_transaction) - Delete Transaction (
delete_transaction) - Edit Transaction (
edit_transaction) - List Transactions (
list) - Get Transaction (
get) - Find Transactions (
find) - Clear All Transactions (
clear_transactions)
- Add Transaction (
- Budget Management
- Set Budget (
set_budget) - Clear Budget (
clear_budget) - Get Budget (
get_budget)
- Set Budget (
- Financial Statistics
- Get Total Expenditure (
get_total_expenditure) - Summary Statistics (
summary)
- Get Total Expenditure (
- General Utility
- Show Help (
help) - Reset UniCa$h (
reset_unicash) - Exit UniCa$h (
exit)
- Show Help (
The instructions for the usage of each command within each feature group are elaborated in the sections below.
For the command examples mentioned herein, you can assume that Output refers to the text
shown in the Results Display, unless stated otherwise.
Transaction Management
Transaction management allows users to directly manage their personal finances by adding, editing, deleting, and finding transactions, among other management features.
Add Transaction
Adds a new Transaction to UniCa$h.
Command: add_transaction n/NAME type/TYPE amt/AMOUNT [dt/DATETIME] [l/LOCATION] [c/CATEGORY]
Take note the following prefixes definition overrides the one in the prefix types section
| Prefix | Constraints | Remarks | Valid | Invalid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
l/(Location of transaction) |
At least 1 character but no more than 500 characters. Only supports alphanumeric characters, spaces, (, ), _, @, -, #, &, ., and , characters. |
If no value is provided, i.e. l/, then it defaults to -. |
l/l/NTUC @ UTown |
l/Two ^ |
Command Words Accepted: add_transaction, add, at (case-insensitive)
There is a limit of 5
Category that can be added to a Transaction. There is a limit of 100,000 transactions you can add to UniCa$h.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Add transaction with name, amount, type, datetime, location and a category.
Input:
add_transaction n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 dt/18-08-2023 19:30 l/ntuc c/householdOutput:
New transaction added: Name: Buying groceries; Type: expense; Amount: $300.00; Date: 18 Aug 2023 19:30; Location: ntuc; Categories: #household
Example 2
Case: Add transaction with name, amount and type.
Input:
add_transaction n/Working type/income amt/8000Output:
New transaction added: Name: Working; Type: income; Amount: $8000.00; Date: 28 Oct 2023 19:01; Location: -; Categories:Remarks: The value of the
Dateoutput as shown above could be different from the one displayed in your application. Refer to prefix types section for further elaboration on the omission of thedt/prefix.
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Missing compulsory fields.
Input:
add_transactionOutput:
Invalid command format! add, add_transaction, at: Adds a transaction to UniCa$h. Parameters: n/NAME type/TYPE amt/AMOUNT dt/DATETIME l/LOCATION [c/CATEGORY]... Example: add_transaction n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 dt/18-08-2023 19:30 l/ntuc c/household
Example 2
Case: Duplicate categories with valid compulsory fields.
Input:
add_transaction n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 c/household c/householdOutput:
All categories must be case-insensitively unique, duplicate categories are not allowed.
Example 3
Case: More than 5 categories with valid compulsory fields.
Input:
add_transaction n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 c/household c/entertainment c/education c/fun c/school c/testOutput:
There should only be a maximum of 5 unique categories.
Example 4
Case: More than 100,000 transactions added.
Precondition: UniCa$h already has
100,000transactions stored.Input:
add n/test amt/300 type/expenseOutput:
UniCa$h supports up to a maximum of 100,000 transactions.
Edit Transaction
Edits an existing transaction in UniCa$h.
Command: edit_transaction INDEX [n/NAME] [type/TYPE] [amt/AMOUNT] [dt/DATETIME] [l/LOCATION] [c/CATEGORY]
Command Words Accepted: edit_transaction, edit, et (case-insensitive)
Similar to the Add command, there is a limit of 5
Category that can be added to a Transaction. Important notes:
- The value of
INDEXprovided must be between 1 and the total number of available transactions (inclusive). - While all options besides
INDEXare optional, you must specify at least one field you wish to edit (i.e.Name,Type,Amount,Datetime,Location, orCategory). - If the
Name,Type, orAmountoptions are present in the edit command, the values provided for these options cannot be empty. (See Failed Execution (Example 3) below) - Specially for the Edit feature: Empty values are allowed for
Datetime,Location, andCategory. If these options are provided in the edit command but left empty, the default values that these fields will take are stated in the table below. (See Successful Execution (Example 3) below) - The
INDEXoption must be specified first. The order in which you specify the other options does not matter. - Editing a transaction’s category will result in the replacement of all existing categories.
- For example, in the case of a
Transactionwith two existing categories (Entertainment and Hobbies), editing it withedit INDEX c/Educationwill replace all existing categories, leaving the transaction with a single category, “Education”.
- For example, in the case of a
Default Values for Blank Options:
| Option Name | Default Value |
|---|---|
| INDEX | (NA) |
| n/ | (NA) |
| type/ | (NA) |
| amt/ | (NA) |
| dt/ | Current date time of system’s clock |
| l/ | - |
| c/ | (Blank) |
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Edit an existing transaction’s name, amount, type, datetime, location and categories.
Input:
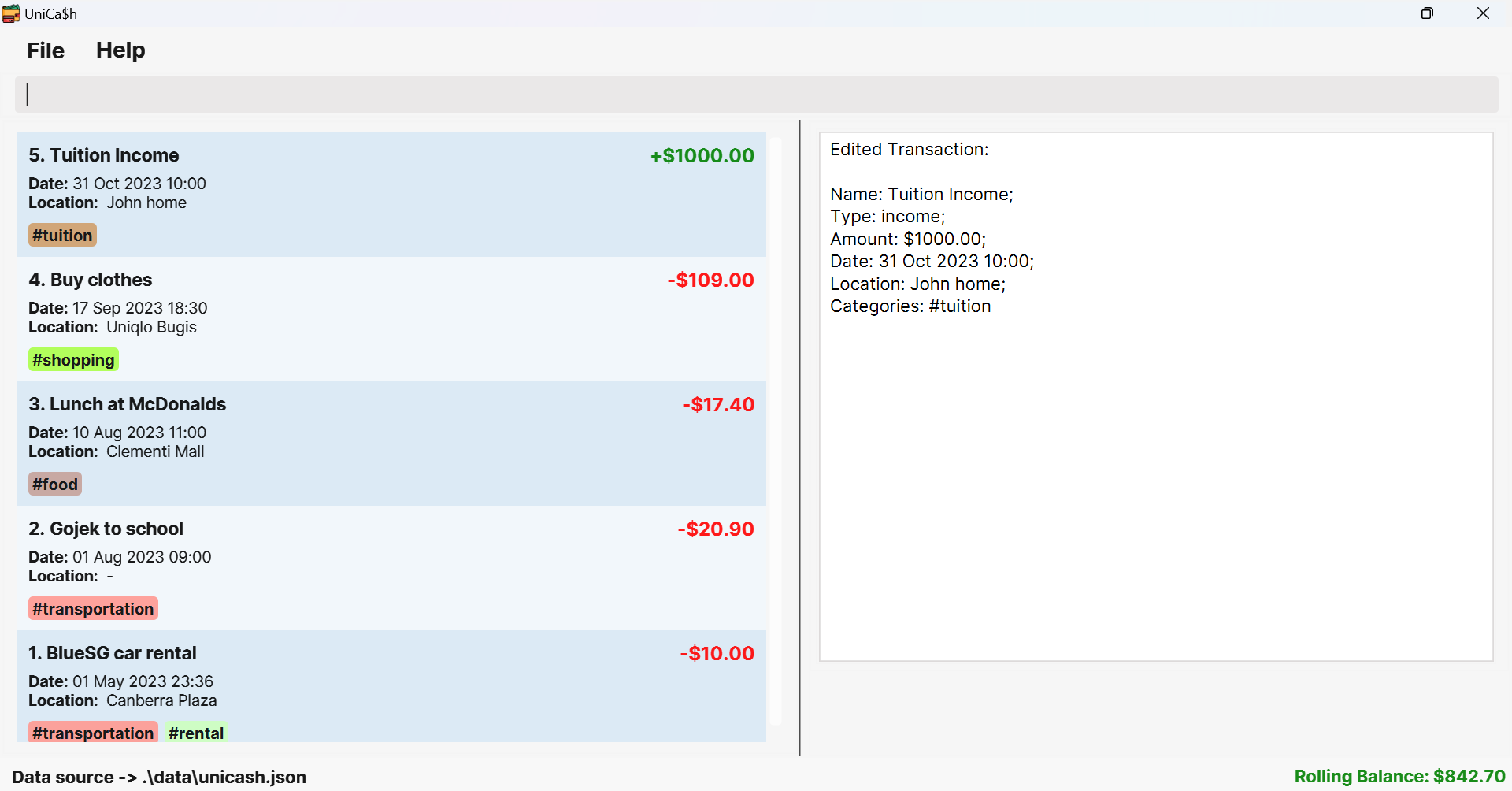
edit_transaction 5 n/Tuition Income type/income amt/1000 dt/2023-10-31 10:00 l/John home c/tuitionOutput:
Edited Transaction: Name: Tuition Income; Type: income; Amount: $1000.00; Date: 31 Oct 2023 10:00; Location: John home; Categories: #tuition
Example 2
Case: Edit an existing transaction’s datetime and amount only.
Input:
edit_transaction 5 dt/31 Oct 2023 12:00 amt/1200Output:
Edited Transaction: Name: Tuition Income; Type: income; Amount: $1200.00; Date: 31 Oct 2023 12:00; Location: John home; Categories: #tuition
Example 3
Case: Edit an existing transaction’s location and categories to default.
Input:
edit_transaction 5 l/ c/Output:
Edited Transaction: Name: Tuition Income; Type: income; Amount: $1200.00; Date: 31 Oct 2023 12:00; Location: -; Categories:
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: No attributes to edit
Input:
edit_transaction 5Output:
At least one field to edit must be provided.
Example 2
Case: No index provided
Input:
edit_transaction n/DonationOutput:
Invalid command format! edit_transaction: Edits the details of the transaction identified by the index number used in the displayed transaction list. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Parameters: [n/Name] [type/Type] [amt/Amount] [dt/DateTime] [l/Location] [c/Category]... Example: edit_transaction 1 n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 dt/18-08-2023 19:30 l/NTUC c/Food
Example 3
Case: Attempting to leave compulsory field (E.g.
name) blankInput:
edit_transaction 5 n/Output:
Names should only contain alphanumeric characters, spaces, (, ), _, @, -, #, &, ., and ',', up to 500 characters and it should not be blank
Example 4
Case: There are only 5 transactions, but the user tries to edit expense 6
Input:
edit_transaction 6 n/Dog foodOutput:
The transaction index provided is invalid
Example 5
Case: Wrong input format (e.g.
Datetimeis not specified in any of the accepted formats)Input:
edit_transaction 5 dt/23 March 2023 8:15pmOutput:
DateTime should be in either of the following formats: 1. dd-MM-uuuu HH:mm 2. uuuu-MM-dd HH:mm 3. dd MMM uuuu HH:mm
Delete Transaction
Deletes a Transaction from UniCa$h.
Command: delete_transaction INDEX
Command Words Accepted: delete_transaction, delete, del (all case-insensitive)
Command Argument: INDEX is the displayed transaction index
of the transaction to be deleted, as shown in the currently displayed Transactions List.
| Arguments | Optional? | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
INDEX |
No | Transaction index of the transaction to be deleted |
INDEX constraints for which you can refer to the
command breakdown’s Argument Types section. You can also refer to the
UI Layout’s Transaction Card section to learn about the transaction index values that
can change based on the current Transactions List configuration.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Delete a transaction with the correctly specified
INDEX.Input:
delete_transaction 1Output:
Deleted Transaction: Name: Evening with friends; Type: expense; Amount: $49.50; Date: 17 Sep 2023 00:00; Location: Clarke Quay; Categories: #social
delete command can be triggered even if a transaction is out of the visible window
as long as that particular transactions exists in the current Transactions List
configuration.
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Missing compulsory fields i.e.
INDEXInput:
delete_transactionOutput:
Invalid command format! delete, delete_transaction, del: Deletes the transaction identified by the index number used in the displayed transaction list. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: delete_transaction 1
Example 2
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as10when only5transactions are present in the currentTransaction Listconfiguration.Input:
delete_transaction 10Output:
The transaction index provided is invalid
Example 3
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as a negative numberInputs:
delete_transaction -1Output:
Invalid command format! delete, delete_transaction, del: Deletes the transaction identified by the index number used in the displayed transaction list. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: delete_transaction 1
Example 4
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as a number larger thanInteger.MAX_VALUEInputs:
delete_transaction 10000000000000000Output:
Invalid command format! delete, delete_transaction, del: Deletes the transaction identified by the index number used in the displayed transaction list. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: delete_transaction 1
Get Transaction
Retrieves a Transaction from UniCa$h.
Command: get INDEX
Command Words Accepted: get, g (all case-insensitive)
Command Argument: INDEX is the displayed transaction index
of the transaction to be retrieved, as shown in the currently displayed Transactions List.
| Arguments | Optional? | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
INDEX |
No | Transaction index of the transaction to be retrieved |
INDEX constraints for which you can refer to the
command breakdown’s Argument Types section. You can also refer to the
UI Layout’s Transaction Card section in the Developer Guide
to learn about the transaction index values that can change based on the current Transactions List configuration.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Retrieve a transaction with the correctly specified
INDEX.Input:
get 5Output:
Transaction 5 retrieved: Name: Taxi; Type: expense; Amount: $20.00; Date: 18 Sep 2023 11:30; Location: Bugis; Categories: #transport
get command can be triggered even if a transaction is out of the visible window
as long as that particular transactions exists in the current Transactions List
configuration.
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Missing compulsory fields i.e.
INDEXInput:
getOutput:
Invalid command format! get, g: Displays expanded details of a specific transaction. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: get 2
Example 2
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as10when only5transactions are present in the currentTransaction ListconfigurationInput:
get 10Output:
The transaction index provided is invalid
Example 3
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as a negative numberInputs:
get -1Output:
Invalid command format! get, g: Displays expanded details of a specific transaction. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: get 2
Example 4
Case: Invalid
INDEXprovidedContext:
INDEXgiven as a number larger thanInteger.MAX_VALUEInputs:
get 10000000000000000Output:
Invalid command format! get, g: Displays expanded details of a specific transaction. Argument: Index (must be a positive integer) Example: get 2
Find Transactions
Finds a Transaction in UniCa$h.
Command: find [n/NAME] [l/LOCATION] [c/CATEGORY]
Command Words Accepted: find, search, f (all case-insensitive)
Command Parameters:
| Parameter | Optional? | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| n/ | Yes* | Search keyword for the name of a transaction. |
| l/ | Yes* | Search keyword for the location of a transaction. |
| c/ | Yes* | Search keyword for a category tagged to a transaction |
| Any of the above | Min. one option | At least one option must be specified for the find command |
Important notes:
- While all options are optional, at least one option must be specified in total.
- Only one instance of each option can be specified, i.e.
n/Friends n/Dinneris invalid as the name option is specified more than once. - All keywords specified must match in order for a transaction to be displayed.
- For each keyword, a substring match is required, thus
find n/with friendswill search for transactions whose name contains the string “with friends”. However, an exact full name match is not required thus, a transaction with the nameLunch with friends outsideis still considered a match.
Transactions List
and this filter persists across commands.
Therefore, it is expected that any changes to the
Transactions List after the find command
is used may result in transactions being hidden as they may no longer abide by the filter applied by find.
Use the
list command when this occurs to reset the filter and view all transactions
Successful Execution
Example 1
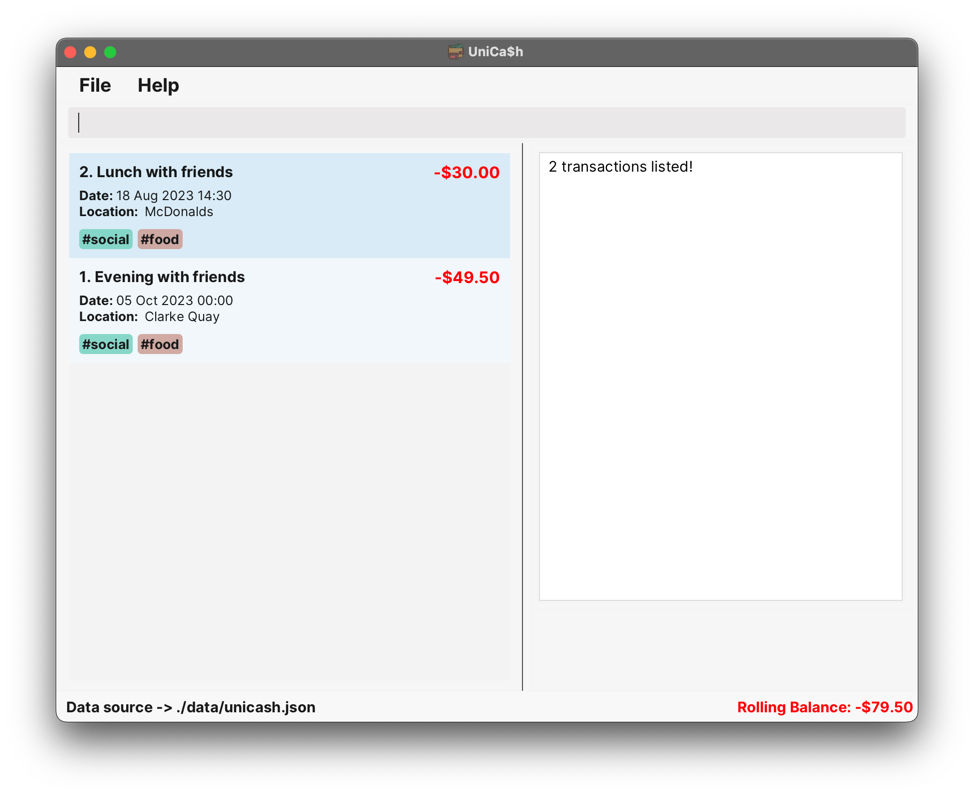
Case: Find a transaction with the correctly specified name option.
Input:
find n/with friendsOutput:
2 transactions listed!
Example 2
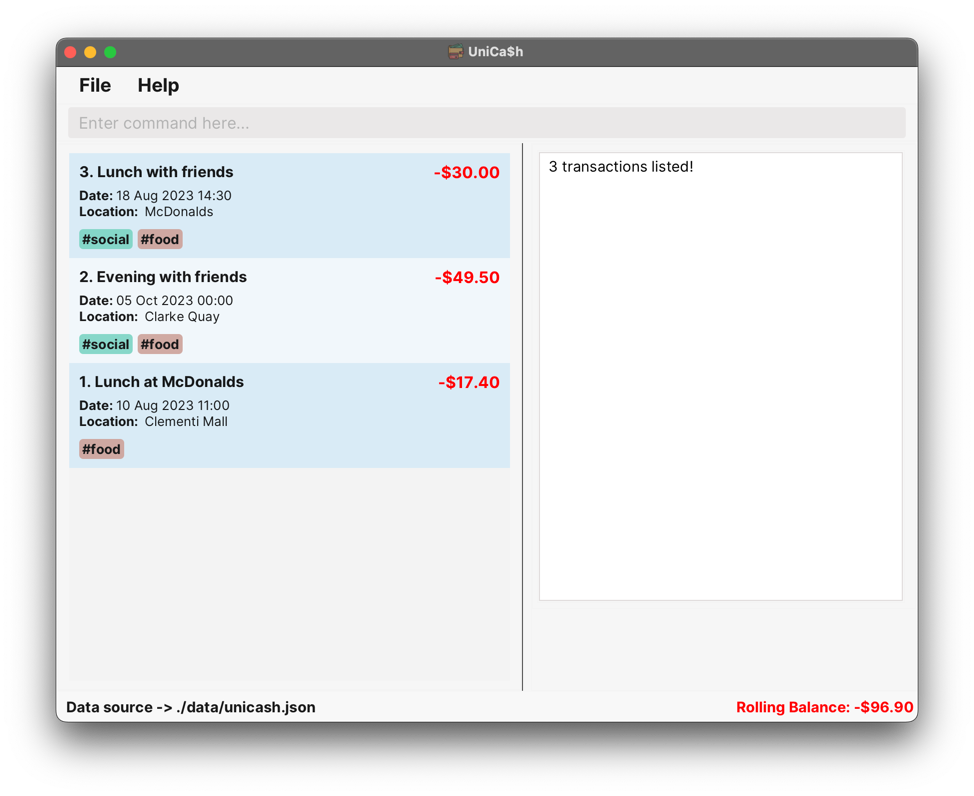
Case: Find a transaction with the correctly specified category option.
Input:
find c/foodOutput:
3 transactions listed!
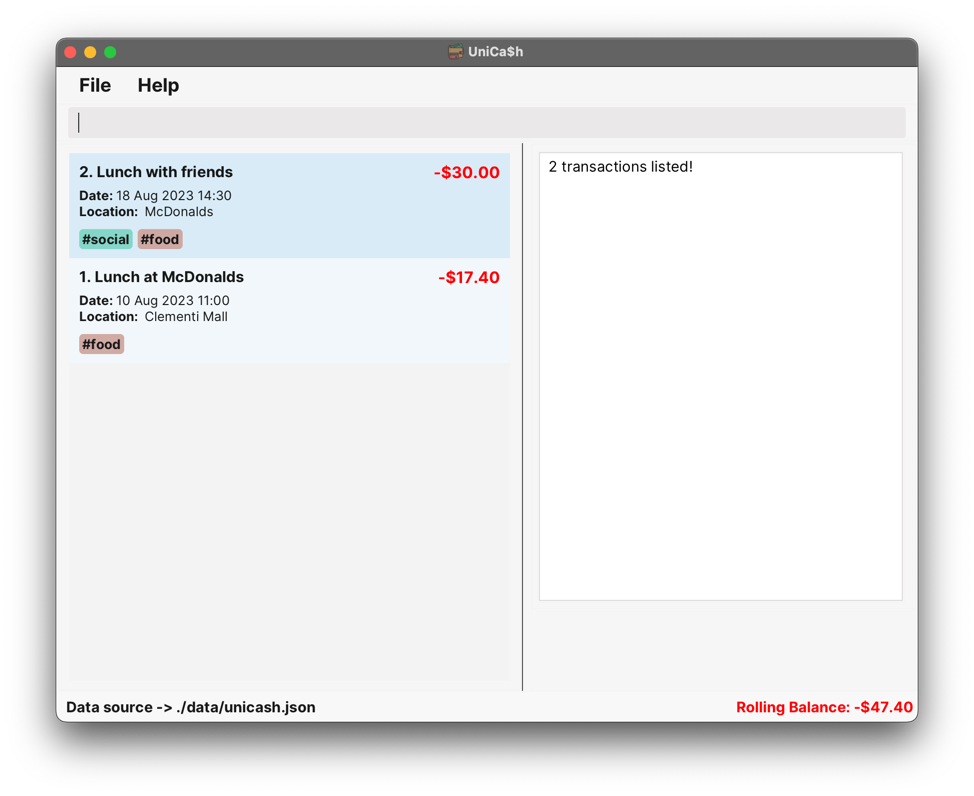
Example 3
Case: Find a transaction with multiple correctly specified options.
Input:
find n/lunch c/foodOutput:
2 transactions listed!
Note that only transactions that match all the given keywords are matched!
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with no parameters
Input:
findOutput:
Invalid command format! find, search, f: Finds all transactions whose properties match all of the specified keywords (case-insensitive) and displays them as a list with index numbers. Only one keyword can be specified for each property and at least one keyword must be provided in total. Parameters: [n/Name] [l/Location] [c/Category] Example: find, search, f n/Buying groceries l/NTUC c/Food
Example 2
Case: Command entered with multiple instances of the same option
Input:
find n/with n/friendsOutput:
Multiple values specified for the following single-valued field(s): n/
Example 3
Case: Command entered with UniCa$h prefixes that are unsupported by
findcommandInput:
find type/expenseOutput:
Invalid command format! find, search, f: Finds all transactions whose properties match all of the specified keywords (case-insensitive) and displays them as a list with index numbers. Only one keyword can be specified for each property and at least one keyword must be provided in total. Parameters: [n/Name] [l/Location] [c/Category] Example: find, search, f n/Buying groceries l/NTUC c/Food
List Transactions
Shows the list of all transactions in UniCa$h.
Command: list
Command Words Accepted: list, ls (case-insensitive)
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Calling the command when there are no existing transactions.
Input:
listOutput:
Listed all transactions.Output:
Note: There are no transactions to display, so the GUI will be empty. This is expected behaviour.
Example 2
Case: Calling the command with existing transactions.
Input:
listOutput:
Listed all transactions.Output:
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with parameters
Input:
list 5Output:
Command not recognised. Try using the command list, list_transactions, ls without any parameters instead.
Clear Transactions
Clears all transactions in UniCa$h.
Command: clear_transactions
Command Words Accepted: clear_transactions only (case-insensitive)
Transactions List
configuration is still subject to any filters applied by find or get_total_expenditure,
which you can read about under the find command section here
or under the get_total_expenditure command section here.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with correct format
Input:
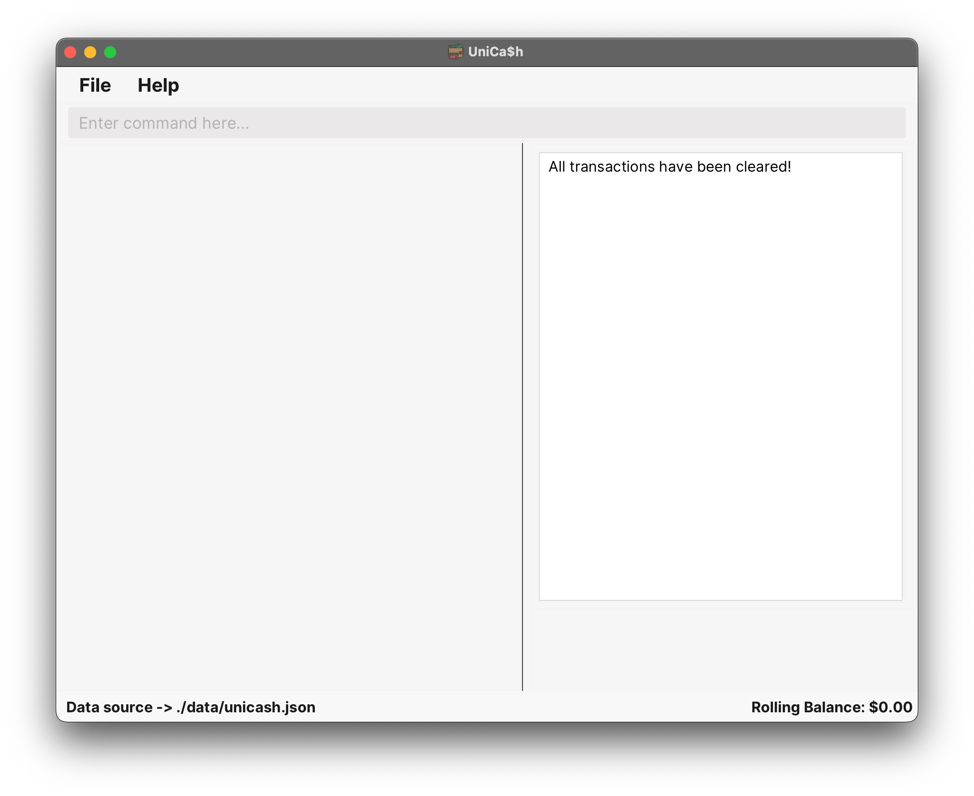
clear_transactionsOutput:
All transactions have been cleared!
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with any trailing text
Input:
clear_transactions asdfg[OR]clear_transactions todayOutput:
Clear transactions command cannot have trailing arguments. Use the command clear_transactions without any trailing arguments.
clear_transactions command is not
meant for batch deletion of specific groups of transaction nor for mass deletion of
transactions present in a particular Transaction List configuration, and that this
command will always delete all transactions in UniCa$h.
Budget Management
The budget serves as an observable metric used to allow users to understand when their expenses over a given interval. They can use this information to better understand if they should be controlling their spending or adjusting their budget.
Set Budget
Sets the user’s budget on UniCa$h to be a given amount and within a given interval.
Command: set_budget amt/Amount interval/Interval
Command Words Accepted: set_budget, sb, budget
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Set budget of $600 for every month.
Input:
set_budget amt/600 interval/monthOutput:
New budget added: Amount: $600.00; Interval: month
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Missing amount.
Input:
set_budget interval/monthOutput:
Invalid command format! set_budget, sb, budget: Sets the user's budget on UniCa$h. Parameters: amt/Amount interval/Interval Example: set_budget amt/300 interval/day
Example 2
Case: Missing interval.
Input:
set_budget amt/600Output:
Invalid command format! set_budget, sb, budget: Sets the user's budget on UniCa$h. Parameters: amt/Amount interval/Interval Example: set_budget amt/300 interval/day
Example 3
Case: No fields.
Input:
set_budgetOutput:
Invalid command format! set_budget, sb, budget: Sets the user's budget on UniCa$h. Parameters: amt/Amount interval/Interval Example: set_budget amt/300 interval/day
Example 4
Case: Negative amount.
Input:
set_budget amt/-123 interval/dayOutput:
Amounts must be within range of [0, 2147483647] and either start with $ or nothing at all
Example 5
Case: Invalid interval value.
Input:
set_budget amt/600 interval/hiOutput:
Interval value must be one of the following: day, week, month
Clear Budget
Clears the user’s budget set in UniCa$h. If no budget is set yet, the user is prompted to set one first instead.
Command: clear_budget
Command Words Accepted: clear_budget, cb (case-insensitive)
clear_budget will not parse any additional argument or parameters. Even if additional argument or parameters are given, any existing budget will be cleared regardless, without any additional effects.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Clear user set budget.
Input:
clear_budgetOutput:
Budget cleared.
Example 2
Case: Clear without set budget.
Input:
clear_budgetOutput:
No budget to clear. Consider using set_budget amt/Amount interval/Interval first!
Get Budget
Retrieves the set budget and the spending over the given interval. If no budget has been set, the user will be prompted to set one first instead.
The user’s spending is calculated by: budget - interval expenses.
Expenses that fall within the interval are included and the total expense is computed relative to the budget.
1. Daily: expenses that occur within the same day of year (i.e. the expenses that occur on day
x are included if today is day x, expenses on day x +/- 1 are not includued)
2. Weekly: expenses that occur within the same week of year. This is dependent on the current year, for more information refer to the documentation here.
3. Monthly: expenses that occur within the same month (i.e. the expenses that occur in September are included if today falls under September)
list command first.
Command: get_budget
Command Words Accepted: get_budget, gb (case-insensitive)
get_budget will not parse any additional argument or parameters. Even if additional argument or parameters are given, no additional effects will be triggered.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Get user’s set budget and spending remainder.
Input:
get_budgetOutput:
Monthly budget of $600.00 Net amount of $585.00
Example 2
Case: Get budget without budget set.
Input:
get_budgetOutput:
No budget set. Use set_budget amt/Amount interval/Interval
Financial Statistics
Get Total Expenditure
Retrieves the total expenditure by month with optional filters for category and year. Also filters the transaction list by the given month, year, and category.
list command first.
Command: get_total_expenditure month/Month [c/Category] [year/Year]
year/ prefix, if not provided, is the current year in which the command is executed.
Command Words Accepted: get_total_expenditure, get_total_exp, gte (case-insensitive)
get_total_expenditure command, like find, creates a filter on the transactions list and this filter persists across commands.
Therefore, it is expected that any changes to the transaction list after
get_total_expenditure may result in transactions being hidden as they may no longer abide by the filter applied by get_total_expenditure.
Use the
list command when this occurs to view all transactions and clear any filters.
For more information on how
get_total_expenditure is computed, refer to the developer guide’s section for it.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Get total expenditure with month only.
Input:
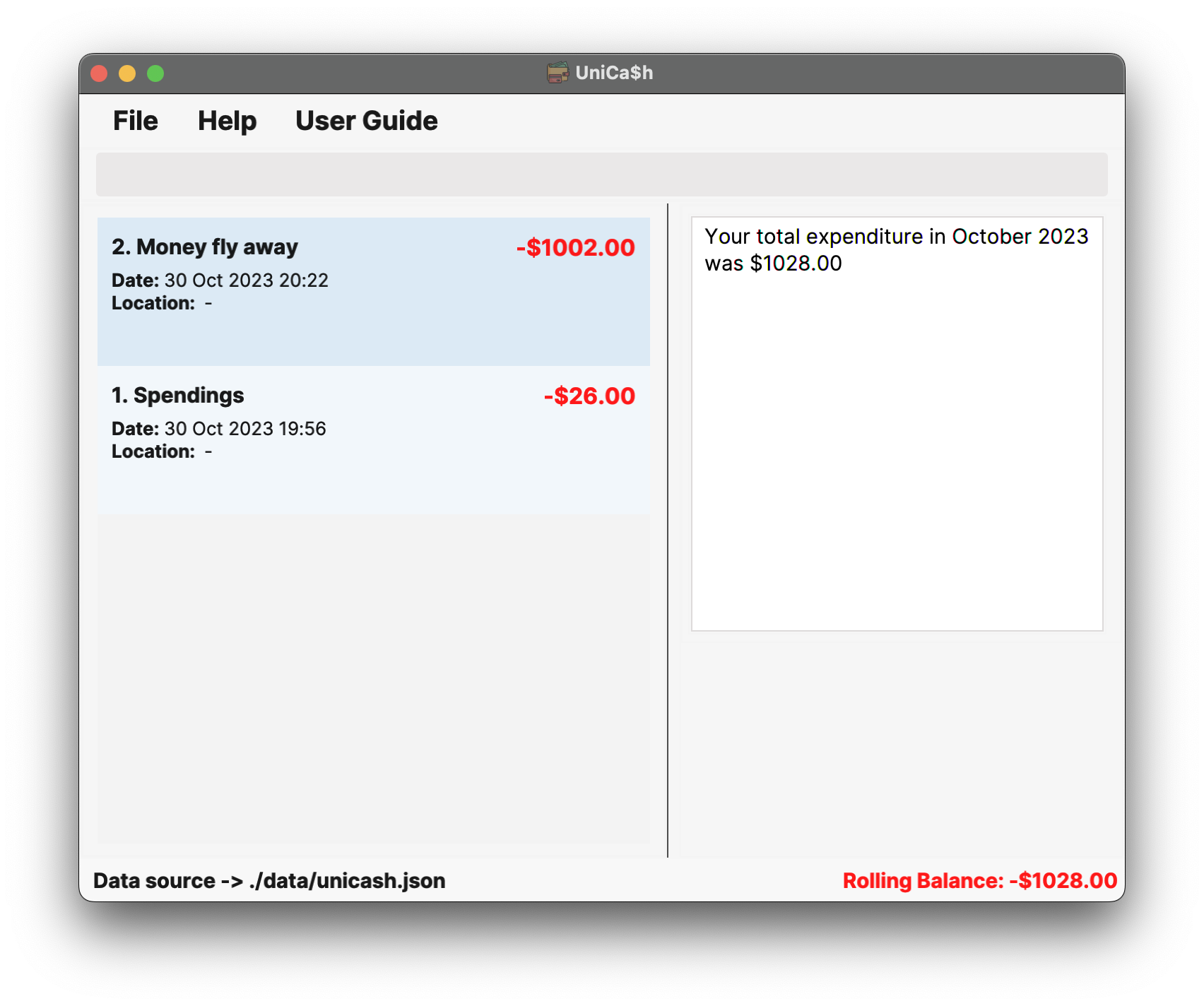
get_total_expenditure month/10Output:
Your total expenditure in October 2023 was $1028.00Note: The year defaults to the current year (2023 in this case) and the transaction list will be filtered
Example 2
Case: Get total expenditure with month and year.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/10 year/2023Output:
Your total expenditure in October 2023 was $1028.00
Example 3
Case: Get total expenditure with month and category.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 c/socialOutput:
Your total expenditure in September 2023 for "social" was $49.50
Example 4
Case: Get total expenditure with month, category, and year.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 c/shopping year/2023Output:
Your total expenditure in September 2023 for "shopping" was $109.00
Example 5
Case: Get total expenditure but no matches.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/1Output:
Your total expenditure in January 2023 was $0.00
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: No month provided.
Input:
get_total_expenditureOutput:
Invalid command format! get_total_expenditure, get_total_exp, gte: Retrieves the total expenditure by month with optional filters for category and year. Parameters: month/Month [c/Category] [year/Year] Example: get_total_expenditure month/10 c/Food year/2006
Example 2
Case: Negative month.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/-10Output:
Month must be between 1 and 12 (inclusive).
Example 3
Case: Month greater than 12.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/14Output:
Month must be between 1 and 12 (inclusive).
Example 4
Case: Month is not an integer.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/hiOutput:
Invalid month value, must be an integer!
Example 5
Case: Year is less than 1920.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 year/1800Output:
Year must be after 1920.
Example 6
Case: Year is not an integer.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 year/hiOutput:
Invalid year value, must be an integer!
Example 7
Case: Category contains non-alphanumeric characters.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 c/@123Output:
Category names should be alphanumeric and up to 15 characters long.
Example 8
Case: Category is blank.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 c/Output:
Category names should be alphanumeric and up to 15 characters long.
Example 9
Case: Category length is greater than 15.
Input:
get_total_expenditure month/9 c/abcdefghijklmnopqrsOutput:
Category names should be alphanumeric and up to 15 characters long.
Summary Statistics
Displays a summary of the expenses saved in UniCa$h.
Command: summary
Command Words Accepted: summary (case-insensitive)
summary will be ignored.
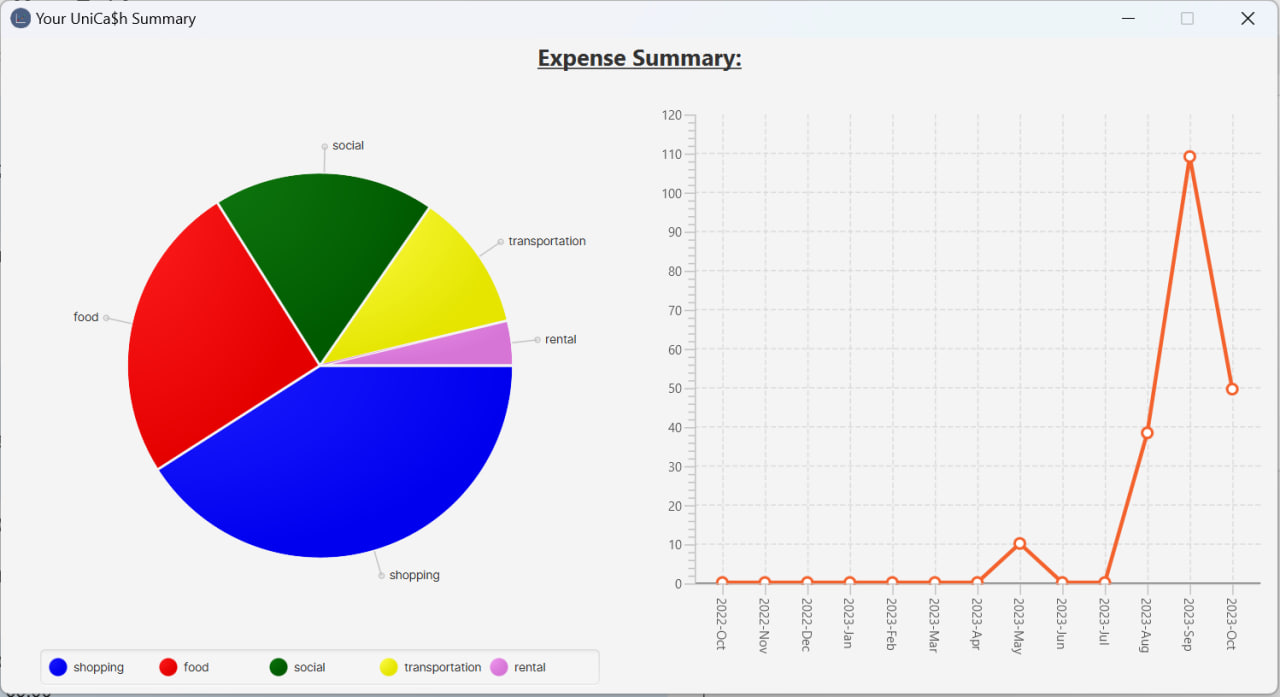
Please be aware that if you open the summary window and subsequently delete all expenses from UniCa$h without closing the summary window, it is intended to stay open until you manually close it. In such a scenario, the summary window will look like the following:
Important notes:
- When making changes to your transactions in UniCa$h, the plots in the summary window will automatically update to reflect your modifications.
This indicates that it is possible for only one plot to have data, while the other does not. (E.g. If there are only expenses recorded from over a year ago, then only the pie chart will display data, while the line chart will not.)
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: There are expenses saved in UniCa$h
Input:
summaryOutput:
The output displayed in the main window is:
Opened UniCa$h summary window.Here is what the summary pop-up window looks like:
Example 2
Case: There are no expenses saved in UniCa$h, and the summary window was not originally opened.
Input:
summaryOutput:
You have no expenses to summarize.
Note: The summary pop-up window does not appear.
General Utility
Help
Get help for UniCa$h.
Command: help COMMAND_WORD
Command Words Accepted: help, h (case-insensitive)
Command Argument: COMMAND_WORD is the command to get help for. If no
argument is specified, a general help message is shown as well as a pop up
containing a link to our User Guide.
COMMAND_WORD, do help with no arguments
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Get general help.
Input:
helpOutput:
Welcome to UniCa$h! For more detailed help on a command: help COMMAND_WORD Available Commands: add delete edit list find get get_total_expenditure summary set_budget get_budget clear_budget clear_transactions reset_unicash help exitThe following output is shown as well as the popup.
Example 2
Case: Get general for a specific command.
Input:
help add_transactionOutput:
add, add_transaction, at: Adds a transaction to UniCa$h. Parameters: n/Name type/Type amt/Amount [dt/DateTime] [l/Location] [c/Category]... Example: add n/Buying groceries type/expense amt/300 dt/18-08-2023 19:30 l/NTUC c/Food
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Get help for an unknown command.
Input:
help fooOutput:
Unknown command help, h: Shows UniCa$h general usage instructions and specific command usage by specifying the command word. Argument: COMMAND_WORD (must be a valid command word present in the help command) Example: help add
Reset UniCash
Resets UniCa$h to its default state with the default transactions
Command: reset_unicash
Command Words Accepted: reset_unicash only (case-insensitive)
Clear Transactions, this command overwrites all existing transactions in UniCa$h.
Thus, as an added layer of safety, the command has no short form alternatives.
It also cannot be followed with any arguments, options, or non-whitespace text.
Transactions List
configuration is still subject to any filters applied by find or get_total_expenditure,
which you can read about under the find command section here
or under the get_total_expenditure command section here.
Successful Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with correct format
Input:
reset_unicashOutput:
UniCa$h has been successfully restored to its original state!
Failed Execution
Example 1
Case: Command entered with random trailing text.
Input:
reset_unicash asdfOutput:
Reset command cannot have trailing arguments. Use the command reset_unicash without any trailing arguments.
Exit UniCa$h
Exit the UniCa$h application.
Command: exit
Command Words Accepted: exit, quit, bye (case-insensitive)
Summary
| Action | Command | |
|---|---|---|
| Add Transaction | add_transaction n/Name type/Type amt/Amount [dt/Datetime] [l/Location] [c/Category]... |
|
| Delete Transaction | delete_transaction INDEX |
|
| Delete All Transactions | clear_transactions |
|
| Edit Transaction | edit_transaction INDEX [n/Name] [type/Type] [amt/Amount] [dt/Datetime] [l/Location] [c/Category]... |
|
| List All Transactions | list |
|
| Find Transactions | find [n/Name] [c/Category] [l/Location] |
|
| Get Total Expenditure | get_total_expenditure month/Month [c/Category] [year/Year] |
|
| Summary Statistics | summary |
|
| Set Budget | set_budget amt/Amount interval/Interval |
|
| Clear Budget | clear_budget |
|
| Get Budget | get_budget |
|
| Reset UniCa$h to default | reset_unicash |
|
| Show Help Window | help |
|
| Show Welcome Message with Summary | help |
|
| Show Command Specific Help | help [COMMAND_WORD] |
Known Issues
- Hard to see scrollbar
- Help pop-up window shifts to the bottom left corner of the screen before re-centering on
helpcommand. Steps to reproduce the issue:- Type help in the command box.
- Shift the pop-up window to anywhere on the screen.
- Close the pop-up window.
- Type help in the command box again.
- The pop-up window will shift to the bottom left corner before re-centering itself.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous UniCa$h home folder.
Acknowledgements
This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative.
The UniCa$h App icon is an open source icon named “wallet”, available for personal and commercial uses, sourced from here.
UniCa$h uses the Inter font throughout, licensed under the Open Font License and available for personal and commercial uses, sourced from here.
Terminology
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Transaction | Represents both an expense or an income. Expenses cause a net loss while incomes cause a net gain |
| Expenditure | Total amount for transactions labelled as “expense” |
| Budget | Observable metric on expenditure, tracking daily/weekly/monthly (only one) expense relative to preset budget amount |